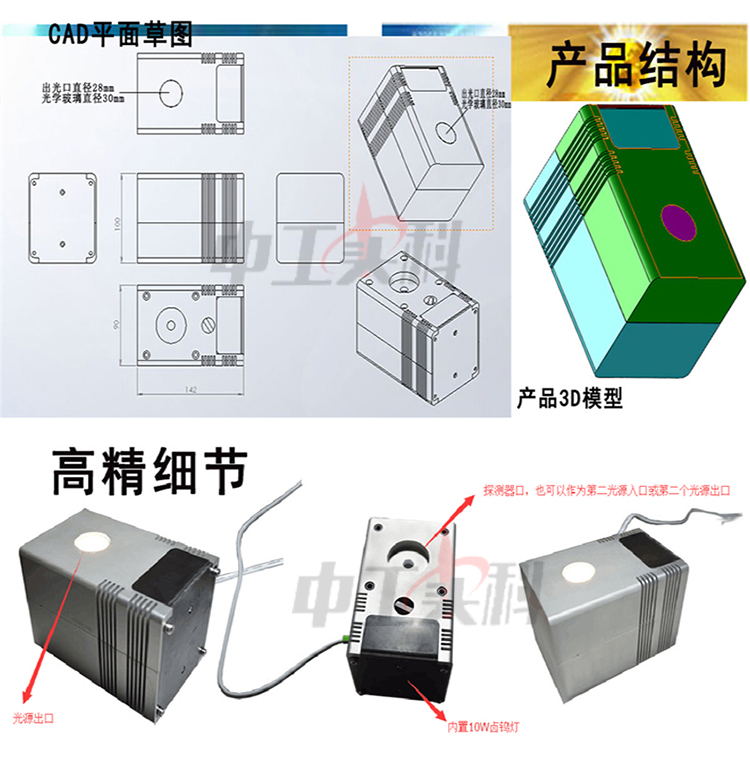
Application of integrating sphere uniform light source system: it is used for the calibration of imaging systems and devices in the laboratory.
Integrating sphere is a hollow sphere whose inner wall is coated with white diffuse reflective material, also known as photometric sphere, luminous flux sphere, etc. One or several window holes are opened on the ball wall as light inlet holes and receiving holes for placing light receiving devices. The inner wall of the integrating sphere is a good sphere, and its deviation from the ideal sphere is usually required to be no more than 0.2% of the inner diameter. The inner wall of the ball is coated with ideal diffuse reflection material, that is, the material with diffuse reflection coefficient close to 1. The commonly used material is barium sulfate, which is evenly mixed with colloidal adhesive and sprayed on the inner wall. The spectral reflectance of barium sulfate coating in the visible spectrum range is more than 99%. In this way, the light entering the integrating sphere is reflected many times through the inner wall coating to form a uniform illumination on the inner wall.
Basic principle of integrating sphere:
The light is collected by the integrating sphere through the sampling port, and is evenly scattered in the integrating sphere after multiple reflections. When the integrating sphere is used to measure the luminous flux, the measurement result can be more reliable. The integrating sphere can reduce and eliminate the measurement error caused by the shape of the light, the divergence angle and the response difference at different positions on the detector.